Australia/Israel Review
Five months of Gaza turmoil
Aug 31, 2018 | Seth J. Frantzman

Twelve hours before rocket sirens began wailing in Israel’s south on Aug. 9, Hamas was optimistic about reaching a five-year ceasefire agreement with Israel. Consumer goods would resume flowing through the Kerem Shalom crossing, and in return Hamas would release the Israeli bodies and captives it is holding, as well as halt the kite intifada burning Israel’s fields and forests.
The UN and Egypt were optimistic the ceasefire would come into effect.
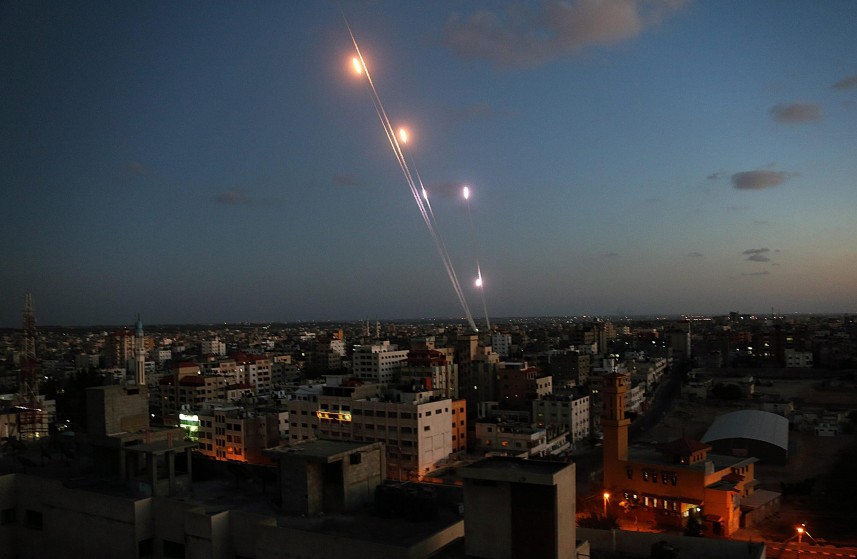
But the ceasefire was not to be. Instead, 180 projectiles were launched overnight – after an incident in which Israel killed two Hamas fighters it mistakenly thought were attacking but were actually involved in military exercises. On Aug. 9 one rocket had even been fired at Beersheba – the largest city in southern Israel – for the first time since 2014.
In retrospect, the signs were clear. Hamas evacuated several border observation posts, raising concerns a military escalation was imminent. This came in the wake of repeated sniper fire over the last month targeting IDF troops. The larger picture is that the conflict between Israel and Hamas has been heating up since March 30, when Hamas launched its “Great March of Return.”
Let’s examine the cascade of events leading to the Aug. 8 blow-up, and their regional political context.
On March 13, Palestinian Authority (PA) Prime Minister Rami Hamdallah and PA intelligence chief Majed Faraj visited Hamas-run Gaza to inaugurate a sewage purification plant. Shortly after Hamdallah’s convoy passed through the Israeli-controlled Erez checkpoint, known to Palestinians as Beit Hanoun, it was targeted by a bombing that the PA blamed on Hamas.
A week later, on March 25, Hamas began firing rockets and ratcheting up tensions with Israel. It appeared that, having failed to achieve reconciliation with the PA, Hamas sought a new round of violence to secure its relevance. This came as the US announced that, on May 14, it would relocate its embassy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem. Hamas’ ostensible response (though actually pre-planned before the US announcement) was the “Great March of Return”, which began on March 30, coinciding with Land Day. The protest was supposed to last until May 14, which Palestinians call Nakba Day, mourning the “disaster” of the 1948 war with Israel which resulted in some 700,000 Arabs becoming refugees.
For two months, Hamas orchestrated massive, violent marches towards Israel’s Gaza security fence. For eight consecutive Fridays, tens of thousands of protesters attempted to breach the barrier. IDF snipers were ordered to fire on the demonstrators who tried to do so, resulting in more than 100 killed and many thousands wounded. The deadliest day was May 14, the day the US opened its embassy; 58 Gazans were killed and 1,200 wounded.
When Hamas found that its fence riots were ineffectual in gaining sympathy in the international community, or even the region, it resorted to an innovative tactic. Initially during the riots and protests, a few Palestinians flew incendiary kites over the border, setting fields ablaze. By July 9, a systematic campaign of launching burning kites into Israel had destroyed 2,800 hectares (6,900 acres) of fields and national parks near Gaza.
At the same time, Hamas was testing Israel with mortar and rocket fire. On May 29, 28 mortars were fired, the largest barrage since Operation Protective Edge in 2014. By the end of the day, more than 70 projectiles had been fired. This began a period from June through to August, of increasing rocket fire, Israeli retaliation and warnings from Jerusalem that war was imminent. On July 18, a barrage of rockets led to the largest Israeli air strikes on Gaza since 2014.
Jerusalem reportedly told Cairo, the main conduit in discussions with Hamas, that war would break out in two hours if the rockets were not halted. But Jerusalem’s toothless warnings have become quotidian. On July 20, Defence Minister Avigdor Lieberman warned of a long war. Israel had threatened Hamas leaders on May 14 during the fence riots. On May 29, Israel also warned it was “closer than ever” to conflict. On July 27, Israel again threatened an expanded conflict with a potential ground operation in Gaza.
Hamas’ response was sniper fire against Israel, and on July 20 it succeeded in killing an IDF soldier. Reports indicated that the sniper’s rifle was modified by Iran. The deadly gunfire is part of a pattern of using civilians to cover Hamas fighters’ movements and increased shooting incidents that began in March and continued into August, right up to the latest round of fighting. Israel responded to the sniper fire with tank shelling which demolished observation posts Hamas reportedly used to conceal spotters.
The larger regional picture is that Egypt has been trying hard to rein in Hamas and find a path to a ceasefire. But Egypt is not alone. The PA has sought to isolate Gaza by reducing remittances and payments there. That led to a rare protest on June 13 by Palestinians in Ramallah against the PA. Hamas therefore is not only trying to achieve a ceasefire with Israel, but also to forge a reconciliation agreement with the PA. That’s why the assassination attempt on Hamdallah was important and set the scene for the conflict that began in late March.
Hamas says it wants Israel to end the 10-year blockade of Gaza and to ease restrictions on goods flowing to the coastal enclave. But the US Administration under President Donald Trump is having none of Hamas’ stories about who is to blame for the Strip’s woeful problems. Trump’s diplomatic envoy Jason Greenblatt said in May that Hamas has taken the territory back to the Stone Age. He made similar statements in op-eds and discussions in March and June.
Then in July, Jared Kushner, Greenblatt and US Ambassador to Israel David Friedman authored a piece in the Washington Post, again pressuring Hamas. Hamas sees the US officials as “spokesmen for the Israeli occupation,” as it called them in July. But it’s clear that the US sees sorting out Gaza as a key to its proposed “deal of the century.”
A last piece of the puzzle is Qatar, which has also sought a role in dealing with Gaza. A major investor in the reconstruction of Gaza following the 2014 war – and also a previous backer of Hamas – Qatar’s ruler Amir Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani wants to be relevant. Toward that end, he has sought to play up the chances for discussions with Israel and position his country as playing a positive role.
This is part of the larger struggle Qatar is embroiled in with Egypt and Saudi Arabia. In this sense, Gaza is the “prize” that Washington, Qatar, Egypt, Israel, the UN and the PA are all trying to win. Hamas’ desire to terrorise Israel and thus be relevant, and the fact that Iran is also funding Hamas and wants it to be a thorn in Israel’s side, is part of a larger struggle in which each side seeks some strategic gain from Israel, Hamas and Gaza.
All of those agendas contributed to the rising crescendo of violence that exploded on Aug. 8 and could easily explode again.
Seth Frantzman is the Jerusalem Post’s opinion editor and a writing fellow at the Middle East Forum. © Jerusalem Post (www.jpost.com), reprinted by permission, all rights reserved.
Tags: Gaza, Hamas, Israel, Palestinians