Australia/Israel Review
Is Iran losing the Middle East?
Nov 28, 2019 | Maya Carlin

Could uprisings in Iraq and Lebanon, coupled with US sanctions, permanently impair Iran’s influence in the region?
In the past few weeks, frustrated and fed-up demonstrators have taken to the streets of Lebanon and Iraq to voice grievances against their governments. The perception of Iranian infiltration and influence certainly continues to impact this political shake-up in both regions.
These protests toppled two governments in just three days. Saad Hariri, Lebanon’s Prime Minister, announced his resignation on Oct. 29. Iraq’s President Barham Salih then stated that Prime Minister Adil Abdul-Mahdi had also agreed to resign from office once a successor is decided upon.
In both Iraq and Lebanon, political factions are divided by religions and sects. These government systems are designed to limit sectarian conflicts by ensuring a sharing of power by different communities. However, in both regions, prominent Shi’ite parties are conjoined with Iran. Since protesters are demanding an end to their government’s power-sharing systems, Teheran is in trouble.
Iranian Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei announced via Twitter on Nov. 14 that, “The people [protesters] have justifiable demands, but they should know their demands can only be fulfilled within the legal structure and framework of their country. When the legal structure is disrupted in a country, no action can be carried out.”
This statement, riddled with irony, completely discounts the revolution which birthed the government Khamenei currently leads. The Ayatollah also verified how deeply entrenched Hezbollah has become in Lebanon’s political makeup.
Hezbollah is certainly the Islamic Republic of Iran’s most successful export. For over two decades, Teheran has played the role of puppet-master in Beirut, attempting to counter the influence of its enemies: the US, Israel and Saudi Arabia. Hezbollah’s critical influence in the region was demonstrated during the 2006 war with Israel and with the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps’ (IRGC) intervention in the Syrian conflict.
Hezbollah’s military and political wings work in tandem to export the regime’s disturbing agenda. In 2017, the US State Department identified more than 250 operatives and 150 companies with Hezbollah ties. Last year, the details of Project Cassandra exposed the sophistication and breadth of Hezbollah’s billion-dollar criminal enterprise.
Since Teheran heavily invests in Hezbollah’s role globally, these protests do not bode well for the regime. The Iranian leadership clearly grasps the magnitude of these demonstrations since its officials have attempted to paint them as manifestations of foreign meddling. Khamenei has accused “US and Western intelligence services, with the financial backing of evil countries,” of orchestrating these protests.
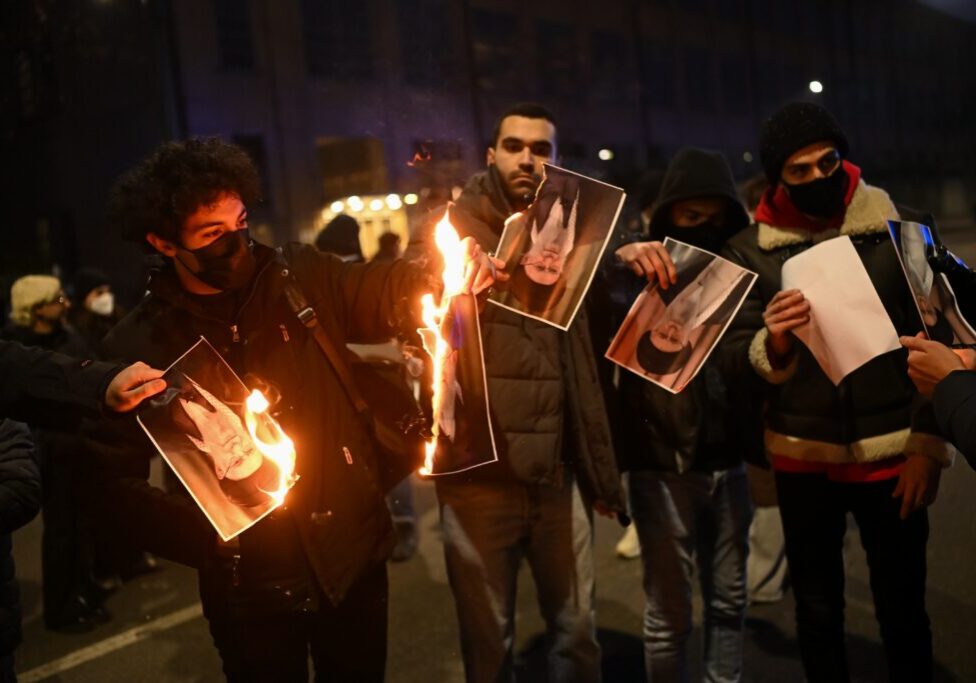
In Iraq, anti-Iran sentiment has monopolised the demonstrations. In Baghdad, protesters were pictured torching an Iranian flag. A few days later, they threw petrol bombs at the Iranian Consulate in Karbala, an important Shi’ite dominated city. The former head of the Iraqi National Archives explained that, “the revolution is not anti-American, it is anti-Iran; it is anti-religion – anti-political religion, not religion as such.”
Pro-Iranian paramilitary forces have violently intervened in recent demonstrations in Iraq. Since Oct. 1, the Iraqi High Commission for Human Rights reports that 301 protesters have been killed, and thousands more injured.
As Teheran continues to dismiss these protests as inauthentic and foreign-led, demonstrators will gain more momentum. While Iran grapples with the economic consequences of Trump’s maximum-pressure campaign, its regional empire will struggle to survive the coupled onslaught of these protests.